
The Internet is a computer network that connects the whole world for sharing data and information. It allows users to access and share information, communicate, and interact with others across the world. The Internet supports a wide range of services, including email, social media, online banking, e-commerce, streaming media, and access to websites and information resources. It is an essential tool for modern communication, education, business, and entertainment.
We get the word “Internet“ from the term “internetwork.” An internetwork is a type of LAN (Local Area Network) and/or WAN (Wide Area Network) that connects multiple networks, or intranets. In an internetwork, hosts use IP addresses to communicate with other hosts on different LANs. The internetwork is made up of many interconnected computers located in various places.
Ancient History of the Internet: In the late 1960s, ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) was developed by the United States Department of Defense’s ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency). ARPANET was the first computer network to use packet switching to connect geographically scattered computers. It was the foundation of the Internet and marked a significant milestone in the history of computing. The first node of ARPANET was established at the University of California, Los Angeles, in 1969. Tim Berners-Lee’s invention of the World Wide Web (WWW) in 1989 revolutionized how information is accessed and shared online.
Table of Contents
Why Internet is Called a Computer Network?
The Internet is called a computer network because it consists of a vast system of interconnected computers and servers that communicate with each other. Here’s why it’s classified as a computer network:
- Interconnection of Devices: The Internet connects millions of computers, servers, and other devices worldwide, allowing them to share data and resources.
- Communication Protocols: It uses standardized communication protocols, such as TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), to facilitate data exchange between devices. These protocols define how data is transmitted and received over the network.
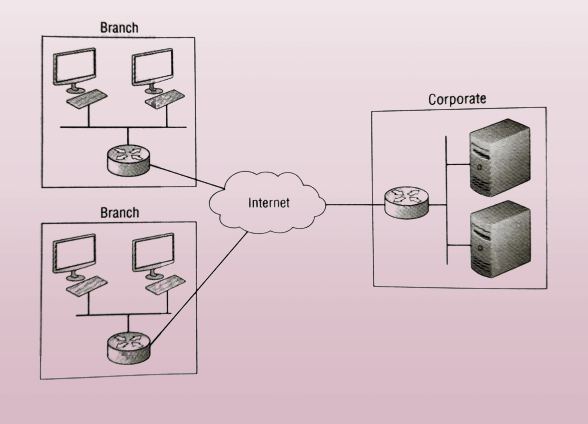
- Network Structure: It has a hierarchical structure of networks, including local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and autonomous systems (AS). These networks are interconnected to form the global Internet.
- Resource Sharing: The primary purpose of it, like any computer network, is to share resources, such as files, applications, and hardware (e.g., printers, storage devices), across multiple users and devices.
- Access to Services: It provides access to a wide range of services, including the World Wide Web, email, file transfer, and online communication, which are typical features of a computer network.
- Infrastructure: The infrastructure of the Internet includes routers, switches, and transmission media (e.g., fiber optics, satellites) that interconnect different network segments and facilitate data routing and transmission.
In essence, the Internet is a massive, global computer network that enables computers and other devices to connect and communicate with each other, making it an integral part of modern networking.
Good Uses of the Internet
- Communication:
- Email and Messaging: Allows instant communication across the globe.
- Social Media: Connects people and communities, fostering relationships and collaboration.
- Video Conferencing: Facilitates remote meetings, virtual classrooms, and online events.
- Education:
- Online Courses: Provides access to a wide range of educational resources and courses from institutions worldwide.
- Research: Enables access to vast amounts of information, academic papers, and research materials.
- E-Libraries: Digital libraries offer access to books, journals, and articles.
- Information Access:
- News: Provides up-to-date news and information on global events.
- Knowledge Sharing: Platforms like Wikipedia and online forums allow users to share and access knowledge on various topics.
- Health Information: Access to medical advice, health tips, and online consultations.
- Entertainment:
- Streaming Services: Offers movies, TV shows, music, and live events.
- Gaming: Provides a platform for online gaming and social interaction through games.
- Social Media and Blogs: A source of entertainment through content creation and sharing.
- E-Commerce:
- Online Shopping: Allows consumers to buy products and services from anywhere.
- Banking and Finance: Facilitates online banking, bill payments, and financial transactions.
- Business Marketing: Provides platforms for businesses to reach a global audience.
- Productivity:
- Cloud Services: Enables storage, data backup, and collaborative work through cloud computing.
- Project Management Tools: Facilitates team collaboration and project tracking.
- Remote Work: Supports telecommuting and remote work opportunities.
Bad Uses of the Internet
- Cybercrime:
- Hacking: Unauthorized access to systems and data.
- Phishing: Fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information.
- Identity Theft: Stealing personal information to commit fraud.
- Privacy Issues:
- Data Breaches: Unauthorized exposure of personal data.
- Surveillance: Unwarranted monitoring by governments or organizations.
- Tracking: Collection of user data without consent.
- Addiction:
- Internet Addiction: Excessive use leading to neglect of personal and professional life.
- Social Media Addiction: Over-reliance on social media platforms, affecting mental health and productivity.
- Gaming Addiction: Excessive gaming leading to negative impacts on daily life.
- Misinformation and Fake News:
- Spread of False Information: Rapid dissemination of unverified or false information.
- Manipulation: Use of misinformation to influence opinions and behaviors.
- Scams: Fraudulent schemes to deceive and exploit people.
- Cyberbullying and Harassment:
- Online Harassment: Bullying and abusive behavior through online platforms.
- Stalking: Persistent and unwanted attention towards individuals.
- Trolling: Deliberate provocation and antagonism in online communities.
- Illegal Activities:
- Piracy: Unauthorized sharing and downloading of copyrighted material.
- Dark Web: Activities like drug trafficking, illegal trading, and illicit services.
- Terrorism: Use of the Internet for radicalization and planning of terrorist activities.
- Health Risks:
- Eye Strain: Prolonged screen time leading to digital eye strain.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity due to excessive internet use.
- Mental Health Issues: Anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues due to internet overuse and social media pressures.
The internet is a powerful tool with vast potential for both positive and negative impacts. Responsible and mindful use is crucial to maximizing its benefits while minimizing its drawbacks. Education on safe internet practices and awareness of potential risks can help users navigate the digital world effectively.
Read More:
- A Complete Guide to MAC Addresses: Definition, Function, and Uses
- Comprehensive Guide to the Types of Computer Networks: LAN, WAN, PAN, and More
- Understanding Network Cabling: A Beginner’s Guide to the Basics of Wiring Standards
- What is a computer? Definition, Inventor, and best uses of it in 2024
- The History of the Computer
- The Classification of a Computer in the 21st Century
- Making a Bootable Pendrive Without Any Software for Installing an Operating System
- Making a Partition in 6 Easy Steps on a Hard Disk
- Hiding a Partition of a Hard Disk for Data Security
- Ultimate Guide to Boot Configuration Data (BCD Editor) Store Editor: How to Manage and Troubleshoot Boot Settings in Windows
- Binary Code Basics: How Computers Use 0s and 1s to Communicate
- How to Fix Keyboard Hardware Issues: Repair Non-Working Keys Easily
FAQs
Q1: What is the Internet, and how does it work?
Ans: The Internet is a global network of computers connected by cables and wireless signals, exchanging data via protocols like TCP/IP.
Q2: Who invented the Internet, and when?
Ans: The Internet evolved from ARPANET, developed in the late 1960s by researchers like Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn.
Q3: What are the main uses of the Internet today?
Ans: It is used for communication, information retrieval, entertainment, online shopping, and social networking.
Q4: How has the Internet changed communication?
Ans: It allows instant messaging, video calls, and global connectivity, reshaping personal and business interactions.
Q5: What are the different types of Internet connections?
Ans: Common types include DSL, cable, fiber-optic, satellite, and mobile data connections.
Q6: How does the Internet impact daily life?
Ans: It enhances access to information, facilitates work and learning, and offers new ways to socialize and shop.
Q7: What is the role of the Internet in education?
Ans: It provides access to online courses, research materials, and collaborative tools, transforming learning experiences.
Q8: How secure is the information shared on the Internet?
Ans: Security varies; encryption and secure protocols protect data, but risks like hacking and phishing persist.













Leave a Reply